Video & image mapping modes
In C-Play, this aspects is controlled by different “Grid modes”, which can be paired with different “Stereo modes” for stereoscopic content.
Grid mode
This is to indicate that you want to map your video on a physical object, or not.
A “pre-splitted” movie normally has the grid mode “None”, as it is assumed to be already mapped correctly.
But “flat” movies are normally mapped onto a plane grid, fulldome/fisheye onto dome grid and 360 on a sphere.
In C-Play there are two different sphere grids, one for equirectangular video (EQR) and one for equi-angular cubemap video (EAC).
So in summary, the mappings are:
* None (pre-split / prepared content. no mapping)
* Plane (regular flat content with various aspect ratios)
* Dome (180 fulldome/fisheye projection)
* Sphere EQR (360 equirectangular projection)
* Sphere EAC (360 equi-angular cubemap projection)
This option can be changed for the current video in the master header UI: 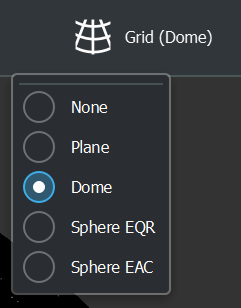
Stereoscopic mode
There are various modes for C-Play to determine how you have mapped your 3D content of your video (or if it is not 3D).
The possible options for this mapping is:
* 2D (mono)
* 3D (side-by-side)
* 3D (top-bottom)
* 3D (top-bottom+flip)
This option can be changed for the current video in the master header UI: 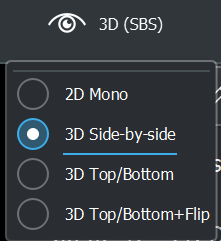
YouTube 360 3D videos
As an example, Google has a cubemap based format for 360 videos, called equi-angular cubemap, which is often used for 360 3D videos downloaded from YouTube. With such a video, you would need to specify user defined settings in C-Play as:
* Sphere (EAC)
* 3D (Top/Bottom+Flip)